We are going to be seeing the different type of joins that are available in SQL.
The four different type of joins which are supported in SQL are:
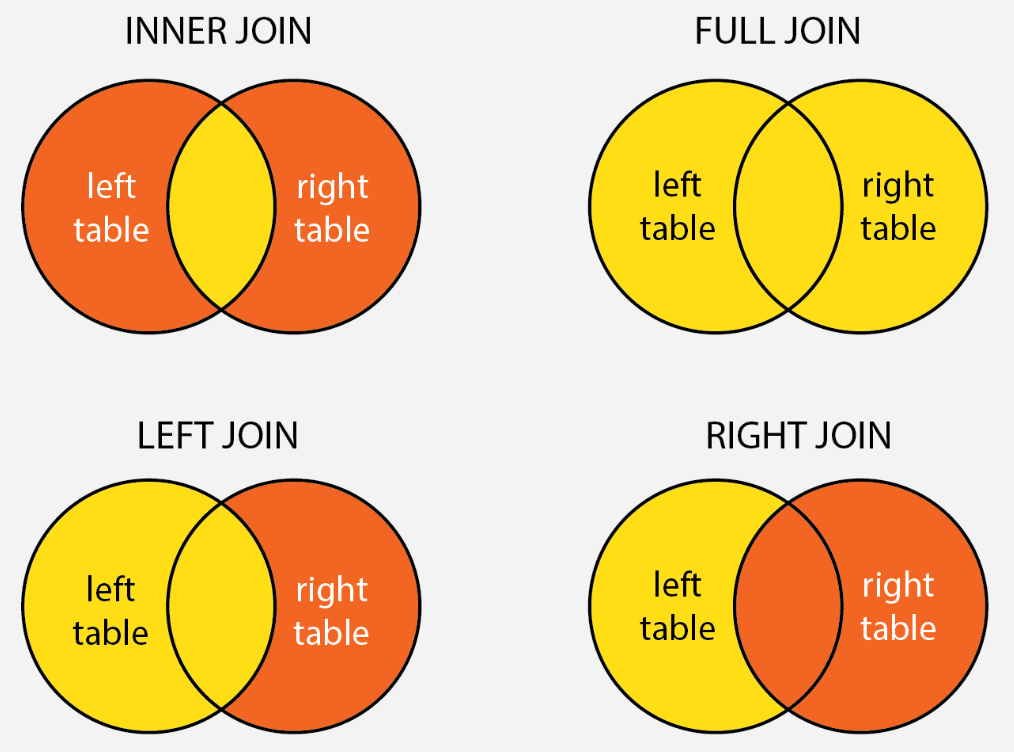
Inner Join – Select common values from both tables.
Left Join – Select all values of left and common of right table.
Right Join – Select all values of right and common values of left table.
Full Join – Select all values from both tables.
Let’s now see the syntax for each:
Generic Syntax:
SELECT COLUMNS_TABLE
FROM LEFT_TABLE
JOIN RIGHT_TABLE
ON JOIN Condition
SELECT name, age, dept_name, dept_id FROM Employee JOIN Deptartment ON Employee.id = Department.dept_id;
The above sql query will fetch columns – Name, Age, Dept_Name, Dept_ID (where dept_id is 2nd Table Column)
condition on which the join is placed is employee table ID = Department table Dept_ID.
Both these fields will act as primary key’s for the respective fields. But in our condition dept_id is the foreign key pointed to primary key ID of employee table.
There is also one more join called as a cross-join which will bring the cartesian value of the two tables which are being joined.
10 rows from table 1 cross joined with 4 rows of table 2 will yield 40 rows in cross joined output.

